C++ Basics
Input/Output
To get an input value and put it into variable x, we can use: cin >> x;, where cin is short for characters in. Moreover, we can also get all remaining text on the current input line and put it into x with getline(cin, x).
To output text, we can use: cout << "desired text";. cout is short for characters out. Additionally, cout << endl starts a new line. Below is an example.
1 | |
In C++ input and output are performed in the form of a sequence of bytes called streams. To enable the program to get input and put output, the first two lines of code should be added at the top of the program to include the necessary library.
Switch statements
Switch statement is an alternative of if-else statements. The program will go from the first case to the last case until it reaches a “break” or reaches the end of the statement. Below is an example. If the condition satisfies, that case’s statement would be executed, and the program will jump to the end. If no case matches, the default case statement will be executed.
1 | |
Character operations
Character operations can be done with functions in the c++ library cctype. Functions include isalpha(c), isdigit(c), isspace(c), isupper(c), islower(c), etc. Below is an example. We included the cctype libary and checked if the two characters are alpha with isalpha(c) function.
1 | |
Floating-point comparison
Floating-point should not be compared using == because some numbers might not be exact due to the bit length limitation. To solve this problem, we can use to compare two floating point numbers. is to compute the absolute value of x. Below is a good example,
1 | |
Enumerations
An enumeration type (enum) is a user-defined data type that declares a name for a new type and possible values for that type which makes the program easy to read and maintain. For example, in the GroceryItem type, there are there values.
1 | |
Arrays, Vectors, and Classes
Vectors
Vector declaration and accessing elements
We declare a vector via:
1 | |
We can access the ith element in the vector using myVector.at(i), but please pay attention to the out of boundary error when choosing the wrong index. A vector’s size() function returns the number of vector elements, and we can iterate through vectors using loops. Below is an example. Also keep in mind that we need to include vector at the top of the file.
1 | |
Vector can be initialized by several ways. Firstly, we can create a vector with three elements, each with value -1 via:
1 | |
We can also initialize each vector element with different values by specifying the initial values in braces {} separated by commas:
1 | |
push_back()function is used to append a new element to the end of a vector.pop_back()function is to remove the last element.back()function is to return the last element without changing the vector.
Below is an example of push_back(), pop_back(), and back().
1 | |
C++ supports Arrays and Vectors for ordered lists.
Arrays are declared as int myList[10], accessed as myList[i].
Vectors are safer than arrays, so using vectors is a good practice.
User-defined function
Functions are a grouping of predefined statements created to reduce redundancy, improve readability, and enable modular and incremental program development. Functions include both function definitions and function calls.
Pass by reference
Variables can be passed by value or passed by reference. In Pass by value, parameters passed as an arguments create its own copy, so any changes made inside the function is made to the copied value not to the original value.
In Pass by reference, parameters passed as an arguments does not create its own copy, it refers to the original value so changes made inside function affect the original value.
A reference is a variable type that refers to another variable. int& maxValRef = usrInput3; declares and initializes the reference variable. Below is another example of pass by reference:
1 | |
Function name overloading
Function name overloading means a program has multiple functions with the same name but different number or types of parameters. For example, there are two PrintDate() functions, and the compiler will determine which function to call based on the argument types.
1 | |
Objects and Classes
The class construct defines a new type that groups data and functions to form an object.
The member access operator, “.”, is to invoke a function on an object.
Private data members are variables that member functions can access but class users cannot.
Below is a complete class definition, and use of that class. Also in this example, we overload the default constructor.
1 | |
While an object’s member function is called using the syntax object.Function(), we can also access the implicitly-passed object pointer via this. For example,
1 | |
Pointers, Memory Allocation and Inheritance
Pointers
Definition
Pointer is a variable that holds the address of a memory. It has a data type. For example, a double pointer holds an address of a double.
A pointer is declared with a * before the pointer’s name; A pointer is initialized with another variable’s address that is obtained by reference operator (&). For example,
1 | |

Dereferencing a pointer
The dereference operator (*) is put behind a pointer variable’s name to get the data value where the pointer variable points. For exaple,
1 | |
Also, a null pointer is nullptr.
Operators: new, delete, and ->
The new operator allocates memory and returns a pointer to the allocated memory.
1 | |
The delete operator deallocates or frees memory.
1 | |
We can also use delete[] operator to free an array. For example:
1 | |
String functions with pointers
The C string library should be included via: #include <cstring>. Strings pass as char*. There are three main string search functions:
-
strchr(sourceStr, searchChar)returns pointer to first occurrence. Else returns null. -
strrchr(sourceStr, searchChar)returns pointer to last occurrence. Else returns null. -
strstr(str1, str2)returns a char pointer pointing to first occurrence of str2 within str1. Else, it returns null if str2 doesn’t exist in str1.
Below is a good example about string and string searching.
1 | |
Dynamic memory allocation
Figure 2 is a summary of constructors and destructors in c++.
Destructor, copy constructor, and copy assignment operator are the so-called rule of three.
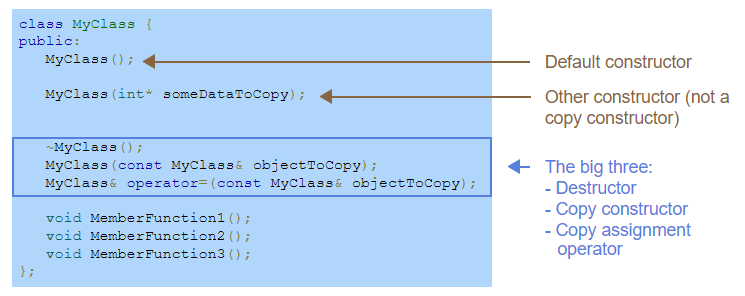
Destructors
**Destructors} cleans up upon object deletion and is called automatically when a variable of that class is destroyed.
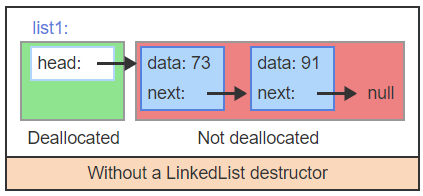
For example, without a destructor, deleting list1 by the code delete list1 only deallocates the list1 object, but not the 2 nodes.
Implementation of a destructor: We can declare the LinkedList class destructors with ~ LinkedList();.
Here is an example of the LinkedList class destructor, called when the list is deleted, frees all nodes. The object’s destructor is called automatically when the object goes out of scope.
1 | |
If we fail to free allocated memory, a memory leak may happen.
Copy constructor
Copy constructor is a constructor that can be called with a single pass by reference argument.
1 | |
Copy assignment operator
The copy assignment operator overloads the built-in function “operator=”.For example,
1 | |
Inheritance and Polymorphism
Inheritance means that the derived class (subclass) inherits the properties of the base class (super class).
There are three kinds of access specifiers, private, protected, and public. Protected allows access by self and derived classes.

Polymorphism allows subclasses to override functionalities of the body class. We need to make the member function in the base class virtual to enable runtime polymorphism.
Another usage for virtual functions is when we can’t or don’t want to implement a method for the base class, and want the implementation being left to the subclass. In this case, we can use pure virtual functions.
A pure virtual function is a virtual function that has no definition in the base class, and all derived classes must override it. The function should always be assigned to 0. An abstract class is a class that cannot be instantiated as an object. Class with one or more pure virtual functions is abstract. For example, the code snippet below is wrong because abstract class can not be instantiated.
1 | |
Note that by defining ComputeArea() to be a “pure virtual function”, Shape is now an abstract class and we can not instantiate it.
Reference
- zyBooks of CSCI 3081W: Program Design and Development, UMN Fall 2022 ↩